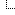mozda i moze da prodje elm ali pitanje je, tacnije treba proveriti prvo koji protokol je na toj masini.
Ako je obd2 odlicno ali ako ide preko k-linije ili vana nece da moze...
ps
ukratko
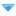
CAN CONNECTION LINES - DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with a CAN (Controller Area Network) system of electrical connections: it involves a software and
hardware solution which is designed to manage the resources on the vehicle efficiently allowing:
? the sharing of information between the various electronic units;
? the intergration of several electronic units through one network;
? a high network information exchange speed;
? advantages in economic terms because there is a considerable reduction in the wiring/connectors inside the vehicle;
? superior standards in terms of quality and reliability.
The advantage of using a CAN system stems from the fact that communication takes place between numerous control units and
consequently the number of signals to be managed is very high.
For this reason the signals travel on a CAN type serial Bus where one wire is high level (H) and the other low level (L); these
signals on the CAN Bus are differential types, i.e. the value assigned to the bit is represented by the difference between the CANH
and CAN-L voltage levels.
The different electronic units which make up the system, known as network nodes, are connected to the CAN by means of
communication interfaces known as transreceivers; these connection interfaces, integrated in the electronic units, constitute the
gate for sending/reading the information at the CAN or at the serial lines.
The exchange of information at CAN type serial lines is only possible using a transmission protocol which is the collection of rules
that allow communication between two or more nodes by means of the exchange of information or "data packages".
The main element of the network is the Body Computer.
The Body Computer node is entrusted with "waking up the network" when the ignition key is turned to the ON position (if there is
a problem with the Body Computer this task is entrusted to the instrument panel).
The Body Computer also carries out the functions of checking the network which make it possible to provide information on:
? the network activities status;
? the functional failure status of the individual electronic units (nodes);
? a possible CAN fault.
The various electronic units process the various signals coming from the corresponding sensors both for their own management
and for other control units to which they are sent via the CAN.
The specific structure adopted for this vehicle consists of two CAN communication networks which connect nodes belonging to two
different areas:
? C-CAN for dynamic vehicle control (high speed): bus CAN-H and CAN-L;
? B-CAN for the management of standard body functions (low speed): BUS CAN-A and CAN-B; the two CAN communication
networks are connected to one another by a gateway for transferring joint information, located in the Body Computer
Node.
Ako je obd2 odlicno ali ako ide preko k-linije ili vana nece da moze...
ps
ukratko
CAN CONNECTION LINES - DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with a CAN (Controller Area Network) system of electrical connections: it involves a software and
hardware solution which is designed to manage the resources on the vehicle efficiently allowing:
? the sharing of information between the various electronic units;
? the intergration of several electronic units through one network;
? a high network information exchange speed;
? advantages in economic terms because there is a considerable reduction in the wiring/connectors inside the vehicle;
? superior standards in terms of quality and reliability.
The advantage of using a CAN system stems from the fact that communication takes place between numerous control units and
consequently the number of signals to be managed is very high.
For this reason the signals travel on a CAN type serial Bus where one wire is high level (H) and the other low level (L); these
signals on the CAN Bus are differential types, i.e. the value assigned to the bit is represented by the difference between the CANH
and CAN-L voltage levels.
The different electronic units which make up the system, known as network nodes, are connected to the CAN by means of
communication interfaces known as transreceivers; these connection interfaces, integrated in the electronic units, constitute the
gate for sending/reading the information at the CAN or at the serial lines.
The exchange of information at CAN type serial lines is only possible using a transmission protocol which is the collection of rules
that allow communication between two or more nodes by means of the exchange of information or "data packages".
The main element of the network is the Body Computer.
The Body Computer node is entrusted with "waking up the network" when the ignition key is turned to the ON position (if there is
a problem with the Body Computer this task is entrusted to the instrument panel).
The Body Computer also carries out the functions of checking the network which make it possible to provide information on:
? the network activities status;
? the functional failure status of the individual electronic units (nodes);
? a possible CAN fault.
The various electronic units process the various signals coming from the corresponding sensors both for their own management
and for other control units to which they are sent via the CAN.
The specific structure adopted for this vehicle consists of two CAN communication networks which connect nodes belonging to two
different areas:
? C-CAN for dynamic vehicle control (high speed): bus CAN-H and CAN-L;
? B-CAN for the management of standard body functions (low speed): BUS CAN-A and CAN-B; the two CAN communication
networks are connected to one another by a gateway for transferring joint information, located in the Body Computer
Node.